
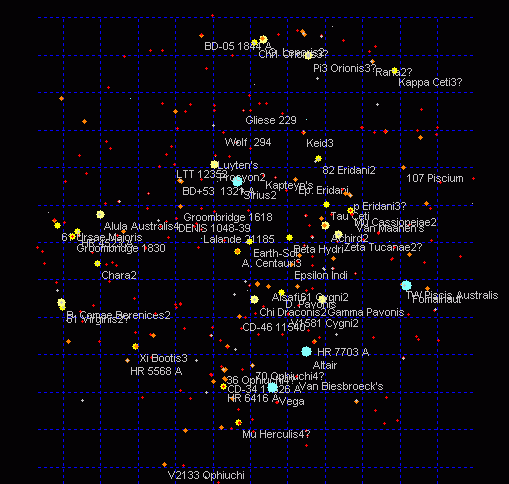

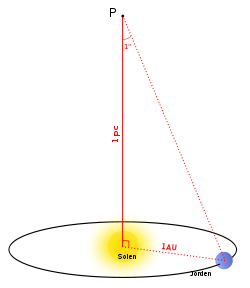
A parsec is equal to about 3.26 light-years or roughly 31 trillion kilometres (19 trillion miles). 1 kilometer (km) is equal 3.2407792669074E-14 parsec use this converter kilometers to miles (km to mi) converter 1 kilometer (km) is equal 0.62118591342441 mile (mi) use this converter miles to kilometers (mi to km) converter 1 mile (mi) is equal 1. This was a big step because suddenly, the speed of light became one of the constants of the universe – and thus, more useful for measuring distances. Unfortunately, like the similarly misused ‘light-year’, the parsec is a unit of length, not of time. (We know now that it isn't – it can be a particle, too).įinally, in 1905, Albert Einstein's theory of special relativity posited that light always travels at the same speed no matter where it is observed from. That speed is a constant, and at the time, most physicists thought of light as a pure wave. In fact, one parsec is approximately 3. Scientists kept refining these estimates, and by the 1860s, Scottish physicist James Clerk Maxwell showed that electromagnetic waves travel at a certain speed in a vacuum. Later, in 1729, James Bradley used a phenomenon called stellar aberration, in which the apparent positions of stars in the sky seem to change slightly depending on the movement of the Earth, to get a closer estimate of light's velocity. (He did come up with an estimate of at least 10 times the speed of sound, but that was very much a guess.)ĭanish astronomer Ole Rømer was able to make an estimate in 1676, using the timing of eclipses of Jupiter's moon Io. The experiment failed, and Galileo could only answer that however fast light was, neither human reflexes nor the clocks at the time were speedy enough to catch it. Galileo attempted it in 1638, and he described an experiment in which one person covers a lantern while another on a tower some distance away tries to time when the light gets there. A parsec is a little over three light years it has nothing to do with times or rates. Īll this depends on knowing the speed of light, and that turns out to be hard to measure because it goes so fast. When we use the light year as a measure of interstellar distance. The sun is 8 light-minutes away, which means it takes light from the sun 8 minutes to reach Earth. Light-years can be divided into light-days, light-hours or even light-seconds, though those units are used less often. British astrophysicist Arthur Eddington, a prominent scientist in the early 20th century, preferred the parsec, calling the light-year "inconvenient." His was a losing battle, however. A parallax-second is the number of arcseconds (1/3600th of a degree) that a star's apparent position shifts when measuring its distance. The light-year competes with the parsec, which stands for parallax-second, and is equal to 3.26 light-years.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
